machinevisiontoolbox.Image.anaglyph
- Image.anaglyph(right, colors='rc', disp=0)
Convert stereo images to an anaglyph image
- Parameters:
right (Image instance) – right image
colors (str, optional) – lens colors (left, right), defaults to ‘rc’
disp (int, optional) – disparity, defaults to 0
- Raises:
ValueErrror – images are not the same size
- Returns:
anaglyph image
- Return type:
Image
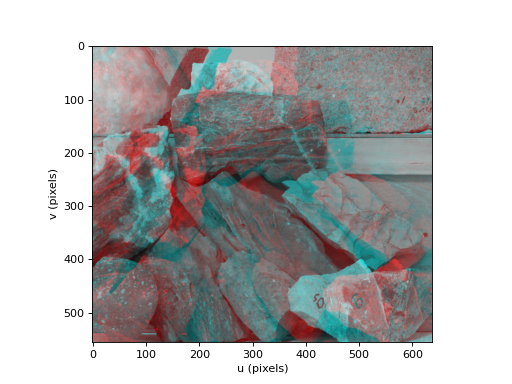
Returns an anaglyph image which combines the two images of a stereo pair by coding them in two different colors. By default the left image is red, and the right image is cyan.
colorsdescribes the lens color coding as a string with 2 letters, the first for left, the second for right, and each is one of:code
color
‘r’
red
‘g’
green
‘b’
green
‘c’
cyan
‘m’
magenta
If
dispis positive the disparity is increased by shifting therightimage to the right. If negative disparity is reduced by shifting therightimage to the left. These adjustments are achieved by trimming the images. Use this option to make the images more natural/comfortable to view, useful if the images were captured with a stereo baseline significantly different to the human eye separation (typically 65mm).Example:
>>> from machinevisiontoolbox import Image >>> left = Image.Read("rocks2-l.png", reduce=2) >>> right = Image.Read("rocks2-r.png", reduce=2) >>> left.anaglyph(right).disp() <matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f3cadd9a0d0>
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)